What Is a Wireless EV Battery Management System?
Marelli’s product manager explains battery management system technology.
July 13, 2023
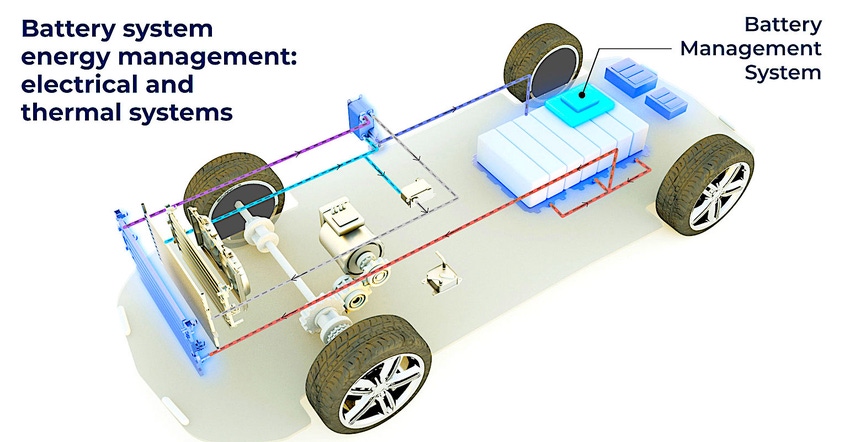
The increasing complexity of electric vehicle design suggests the value of examination of some of the emerging technologies, such as wireless battery management systems. Italian supplier Marelli announced its product in this sector last year, so we thought it would be helpful to chat with Davide Cavaliere, Marelli’s product manager of battery management systems.
The company boasts that the Marelli wBMS can be delivered with a highly sophisticated software application layer that uses advanced algorithms that exploit “Sensor Fusion”. These algorithms estimate several crucial parameters of each battery cell – including State of Charge, State of Health, and State of Power – to ensure a more accurate calculation of the battery's overall status and inform the other components of the powertrain accordingly.
Cavaliere explained in more detail in this Q&A:
Q: What is the battery management system and what are its functions in an electric vehicle?
Davide Cavaliere: The battery management system, also called BMS, is an electronic control unit, that monitors the condition of every single cell located in the battery pack. It is a mandatory device for vehicles equipped with a lithium-ion battery. Battery cells are designed to safely operate in a restricted range of voltage current and temperature. The battery management system constantly monitors these physical quantities to make sure that the limits are not exceeded.
Doing this ensures that the cells don't operate in unsafe conditions and battery cell degradation can be minimized. Other functions include the estimation of the cell's internal state, for example, the state of charge, health, and power.
Q: What are the relevant technologies?
Davide Cavaliere: There are two main types of BMS architecture: centralized and distributed. In a centralized BMS architecture, all cells are connected to the same BMS board. This is an effective solution for battery packs that contain a limited amount of cells, up to 100 cells, according to our experience.
In contrast to that the distributed BMS architecture is composed of two types of boards; a single master board and multiple boards. These boards are located close to the cells, each monitoring from six up to a few dozen cells. Boards are then connected to the master board through a digital communication daisy chain.
This distributed architecture is preferable for middle- and large-scale battery packs used on plug-in hybrid electric vehicles and battery electric vehicles, which have a hundred or more cells connected in series. Marelli has experience with both centralized and distributed BMS architectures, and for the second type we have developed both wired and wireless communication.

Q: How does a wireless BMS work and what are its key elements?
Davide Cavaliere: A wireless BMS is a type of distributed BMS in which the communication between boards is done wirelessly rather than using a wired daisy chain. The data exchange between them is based on a 2.4 gigahertz radio frequency, similar to the communication established between a pair of Bluetooth earphones and a smartphone.
Most of the components used are the same as those of a conventional distributed BMS the only thing that changes is that the communication interface is done using a wireless integrated circuit coupled with an antenna instead of a wired communication transceiver.
Q: What are the advantages of a wireless BMS over a wired solution?
Davide Cavaliere: The main advantage is that communication cables for the daisy chain are no longer needed. Due to that there is an opportunity to reduce cost and weight.
Moreover, battery pack design is simplified since car manufacturers don't need to focus on the design of this part of the wiring harness. This weight reduction also translates into less energy required to move the vehicle and therefore a longer range. In practice, more kilometers can be run with a single charge.
Q: Is wireless technology secure?
Davide Cavaliere: if not designed properly wireless communication is less secure than wired communication because the data is accessible to anyone within the radio wave propagation range. Nevertheless, there are countermeasures such as encryption to authenticate and protect the data during transmission. In addition to that, boards are located inside the battery pack which has a metallic enclosure they are shielded from the external environment.
Q: What factors affect the performance of wireless systems?
Davide Cavaliere: The most important factors for wireless technology are data throughput – megabits per second --, signal strength, and power consumption. These factors are dependent on each other and cannot be all optimized at the same time. For example, increasing data throughput or signal strength comes with an additional power consumption which, since power is absorbed by the battery, should be limited to avoid excessive drain.
Excellence in wireless BMS technology is achieved by optimizing these factors to get fast communication speeds and long range in addition to acceptable power consumption. This requires plenty of experience in choosing the right communication protocol and properly designing the radio frequency part of the system. The antenna and its matching circuit must be optimized to achieve the best performance.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like



