Glass-Fiber PP EV Battery Pack Could Debut in 2024
Sabic’s plastic-intensive EV battery pack concept addresses critical industry needs for flexible design, enhanced performance, greater safety, and improved economics.
May 16, 2021
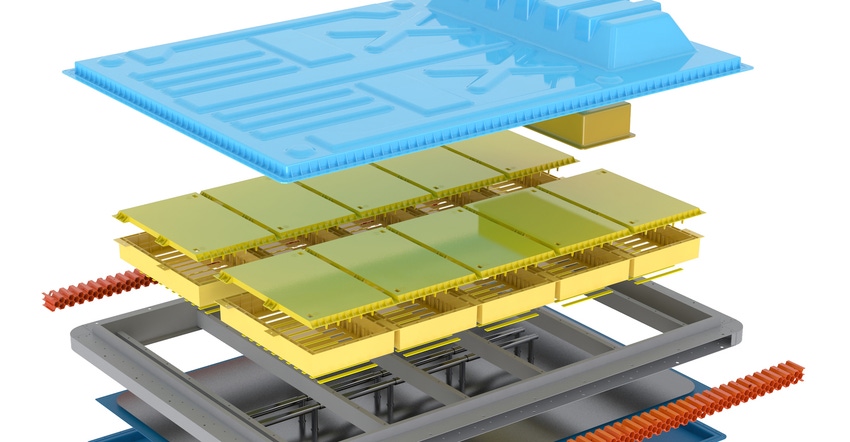
As automakers accelerate their shift to an all-electric future, Sabic continues to develop thermoplastic-based solutions and harness its expertise to help industry optimize the performance of electric vehicles (EVs). Most notably, the company’s automotive business has developed a plastic-intensive EV battery pack concept using a systems-engineering approach. The concept underscores the value of lightweight plastics to address critical industry needs for flexible design, enhanced performance, greater safety, and improved economics.
Compared with conventional battery pack designs using traditional materials such as aluminum and other metals, lightweight thermoplastics potentially can realize 30 to 50% weight savings per component, improve energy density, simplify the assembly process, reduce costs, and improve thermal control and safety.
“Our work on vehicle electrification technologies extends beyond simply pairing materials to individual components within existing designs,” said Abdullah Al-Otaibi, General Manager, ETP & Market Solutions, Sabic. “Our teams of experts take the complete EV battery system and vehicle structure into account so we can properly assist and enable our automotive customers to achieve their most critical vehicle development objectives.”
EV battery pack concept leverages properties and strength of thermoplastics
The Sabic-developed battery pack concept leverages the properties and strength of thermoplastics to improve performance, reduce cost and weight, and support mass production. Highlights include:
Integration of individual batteries into pouch cells placed within a thin-walled housing molded with a 30% glass-fiber-filled, flame-retardant (FR) polypropylene (PP) compound.
Geometric features, such as a double-wall construction, a novel rib pattern, and creative functional integration, all enabled by Sabic thermoplastics to reduce weight and meet structural requirements.
Creative use of the anisotropic thermal conductivity of plastics to optimize thermal management performance.
Integrated plastic-metal hybrid structures with Stamax FR long-glass-fiber PP material for the battery tray to optimize thermal transfer, meet drop test requirements, and absorb the significant impact energy that side frame members can experience.
A battery pack enclosure or cover molded with Stamax FR resin. Use of this material meets the UL94 V-0 flammability rating and allows the cover to be metallized for electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) shielding.
Parts reduction and assembly efficiency, resulting in cost savings, enabled through the inherent design freedom of thermoplastics.
Advancing a collaborative approach across the value chain
Sabic’s focus is to continue growing its expertise and offering to support innovation in EV batteries and additional EV applications. The company has assembled a technology team of chief engineers, research fellows, and senior scientists. Their role is to provide world-class collaborative engagement with customers, development partners, and others across the value chain, from OEMs and tiers to tooling suppliers and testing agencies.
“We are talking about a seismic shift in the automotive ecosystem,” said Al-Otaibi. “The industry can only build and improve upon today’s EV technologies if the entire supply chain is working together. This has long been Sabic’s way of thinking and style of operating. We will continue to pursue collaborative opportunities and partnerships that encourage innovation to thrive.”
Through ongoing work with the industry, Sabic expects several large battery enclosures, molded with its thermoplastics, to be used in production EVs as early as 2024. One plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) model in China is already using the Sabic PP compound instead of aluminum for its battery pack cover, providing weight savings, expanded design freedom, warpage control, and other benefits.
Other EVs in production today around world are using several Sabic materials for components such as cell carriers and housings, battery modules, and battery enclosures.
In addition to developing new materials to meet EV requirements, Sabic is working to enable technologies for large part manufacturing, joining and assembly, crashworthiness, battery thermal management, flame retardancy, electrical properties, and performance testing.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like





