How Toyota's Next-Gen EV Batteries Redefine Speed & Range
Discover the details of Toyota's recently announced EV batteries that will decrease charging times and deliver a driving range of 621 miles.
Toyota recently announced its commitment to the electric vehicle (EV) market. The company is working on a selection of groundbreaking technologies to facilitate its transformation into a mobility company and provide customers with various battery options. Here are Toyota’s next-generation battery technologies, ranging from affordable and widely used ones to those designed for higher performance:
Next-generation battery: Performance version
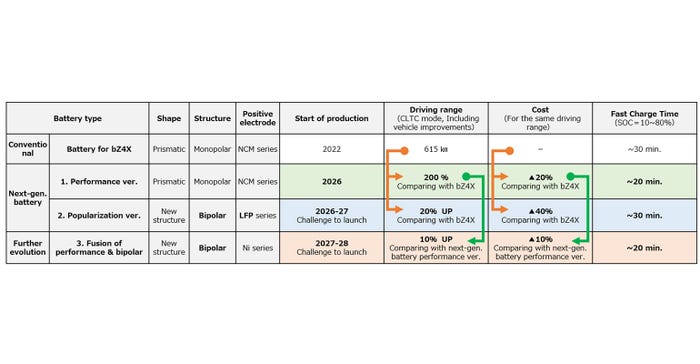
Toyota plans to enhance the mainstream technology—lithium-ion batteries—by improving the energy density of its prismatic/square batteries. The performance version next-generation battery is being developed with Prime Planet Energy & Solutions Corp.
Toyota aims to enhance its vehicle's cruising range by improving its efficiencies, including aerodynamics and weight reduction while achieving a 20% reduction in costs compared to the current bZ4X model, which uses an NMC battery. Additionally, Toyota will try to achieve a quick charge time of 20 minutes or less, all while increasing the battery’s energy density. The next-generation battery electric vehicles (BEVs) to be introduced by Toyota in 2026 will potentially have a cruising range of 621 mi.

Next-generation battery: Popularization version
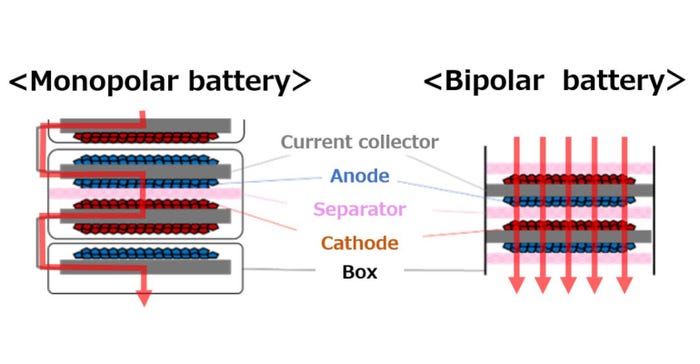
Toyota also stated that it is actively involved in developing affordable, high-quality batteries that will contribute to the broader adoption and growth of BEVs, offering customers a range of battery options. One such advancement is utilizing a bipolar structure battery, previously used in Aqua and Crown hybrid vehicles, which is now being adapted for BEVs.
This battery incorporates cost-effective lithium iron phosphate (LFP) as a material and is expected to be commercially available by 2026–2027. Toyota’s goals include achieving a 20% increase in the vehicle's cruising range, a 40% reduction in cost, and enabling quick recharging within 30 minutes or less (State of Charge (SoC)=10–80%), surpassing the capabilities of the current bZ4X model. Moreover, the company is considering implementing this battery technology in BEVs within the popular price range, ensuring accessibility to a broader range of consumers.
Bipolar lithium-ion battery: High-performance version
Simultaneously with developing a cost-effective battery, Toyota plans to work on a high-performance battery that combines a bipolar structure with a high nickel cathode. According to Toyota, this advanced battery technology is expected to be implemented around 2027–2028.
The upcoming high-performance version will surpass the capabilities of the performance version of the prismatic/square battery, offering notable enhancements. Toyota projects to achieve a 10% increase in the vehicle's cruising range, a 10% reduction in cost, and a rapid charging time of 20 minutes or less (SoC=10–80%). These improvements will give customers outstanding performance and convenience compared to the current battery technology.
All-solid-state batteries for BEVs
Toyota claims to have made a significant technological breakthrough in solid-state batteries (SSB), successfully addressing the long-standing issue of battery durability. Considering this breakthrough, Toyota is evaluating the integration of solid-state batteries into conventional hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and expediting their development as a battery option for BEVs, which are experiencing increasing expectations in the industry.
With SSBs, Toyota is looking at a 20% improvement in cruising range compared to the “performance version” while costs are under scrutiny, aiming for a quick charge time of 10 minutes or less (SOC=10–80%). Toyota is currently developing a mass production method, targeting the "commercialization" of its solid-state batteries between 2027 and 2028. Finally, an SSB with a higher-level specification is under research and development simultaneously, with a 50% more range than the performance version or about 900 miles.
Toyota is moving aggressively on EVs, and its future looks very promising. In fact, according to an analysis article by Seeking Alpha titled “Toyota Trumps Tesla,” Tesla may be overvalued and facing headwinds, while Toyota is seen as a strong competitor with better fundamentals and a more attractive valuation. “Toyota is trumping its biggest competitors and benefitting from demand tailwinds and a strong global network.”
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like





