Why Emerging Trends in Battery Packing Matter
In the battle for market share, EV manufacturers such as ONE, CATL, and Tesla are pushing the boundaries of battery packing.
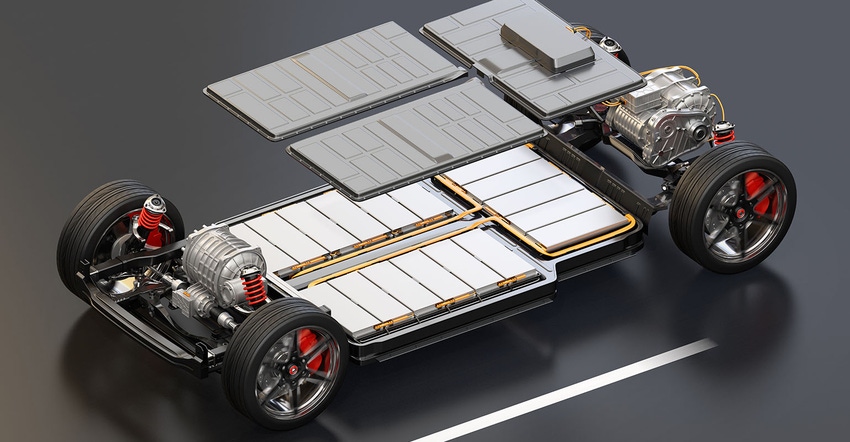
As electric vehicle (EV) adoption accelerates, one of the key focal points of innovation lies in how battery cells are packaged and integrated into these vehicles. Traditionally, EV battery technology has evolved alongside the rapid progression of lithium-ion batteries, paving the way for increased range, energy density, and overall performance. However, recent years have witnessed a paradigm shift in how battery packs are conceptualized and designed.
CTP, CTB, and CTC
The following three approaches are based on how the battery technology is designed and incorporated into the vehicle's structure and have become prominent as the industry explores novel strategies to enhance EV battery efficiency and integration:
1. CTP (Cell-to-Pack): In this approach, individual battery cells are grouped together and directly integrated into larger battery modules or packs. The focus is on creating a cohesive pack that can be easily installed into the vehicle without the need for additional modules or components. This approach can simplify manufacturing, reduce weight and complexity, and potentially improve the overall energy density of the battery system.
The inception of this integration technique dates to 2019, when it was initially introduced by CATL. Since then, other industry players, such as BYD and SVOLT Energy, have sequentially unveiled their unique CTP approaches.
2. CTB (Cell-to-Body): CTB is an innovative approach to battery cell integration in EVs. It represents a significant departure from traditional methods of integrating battery cells and aims to improve space utilization and overall EV performance. CTB is primarily associated with the Chinese automaker BYD, which has pioneered this technology.
CTB technology integrates the battery cells directly within the vehicle's framework. This integration is accomplished by merging the body's floor panel with the upper shell of the battery pack, creating a unified assembly. The passenger cabin is securely sealed using sealant, and the battery's underside is affixed to the vehicle body via mounting points. By utilizing the vehicle's framework as part of the battery system, weight distribution can be optimized, and the available space can be used more efficiently. This integration can benefit the vehicle's stability, performance, and safety.
3. CTC (Cell-to-Chassis): This is an advanced technology and approach in the electric vehicle (EV) industry that involves integrating battery cells directly into the chassis or frame of an electric vehicle. This innovation represents a significant departure from traditional methods of housing batteries in separate enclosures or packs. By doing so, the battery becomes an integral part of the vehicle's architecture, potentially leading to improved design flexibility and overall vehicle performance. CTC simplifies the vehicle's overall design by eliminating the need for a separate battery enclosure. This can reduce manufacturing complexity and costs.
New trends in EV battery packing
Frost & Sullivan explains that there is a trend consisting of a multi-form factor and multi-chemistry with new capabilities, and the following companies are implementing it:
ONE: Their Gemini platform uses a single package that hosts two different chemistries (LFP, NMC) and two different form factors (Large / Small Prismatic).
CATL: Innovative CTP packing with two form factors (Prismatic, Blade) with two chemistries (LFP, NMC). It features a modular battery that is swappable.
Tesla and CATL: Eliminate modules to package cells directly to pack (CTP)/ car frame (CTC).
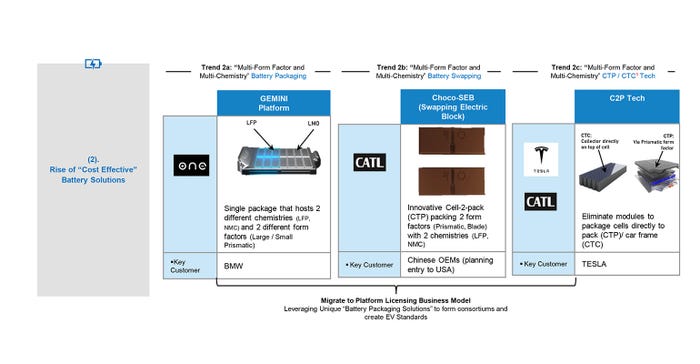
“As the sub $25,000 car market gains prominence on the agenda of automotive CEOs, their focus on innovative cost-saving strategies becomes imperative. This shift in approach is expected to drive the increased utilization of Multi-Form Factor batteries and packaging, a trend exemplified by the advancements made by companies like ONE and CATL” said Benny Daniel, Frost & Sullivan Vice President + Head of Consulting – Mobility Practice Area.
The territory of EV battery packing is undergoing a dynamic transformation with the emergence of cutting-edge technologies such as CTP, CTB, and CTC. These innovations are reshaping how we store and utilize energy in EVs and paving the way for a sustainable and electrified future. New trends align with the industry's goal to make EVs more accessible and cost-effective. However, this diversity can lead to inefficiencies, interoperability issues, and added costs for manufacturers and consumers. It is important to establish standards for battery packaging, ensuring consistency and compatibility across different EV models and brands. Nevertheless, as we witness this convergence of sustainability and affordability, it becomes evident that the future of electric mobility is both promising and inclusive.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like





