Siemens Leverages Electric Arc Sounds to Detect EV Battery Defects
Delve into the world of electric arc localization and its potential to revolutionize battery pack testing in the EV industry.

Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry with their eco-friendly and sustainable nature. However, the production of EVs comes with challenges, one of them being to ensure the functionality and reliability of battery packs through rigorous testing conducted at each production stage.
Performance tests are carried out during pack/system validation, involving charging under specific profiles and dynamic stress tests. Siemens has identified a link between noise and electric arcs that could change how battery testing is done in the EV industry.
Electric arcs and EVs
An electric arc is the movement of electricity that happens between two conductive points. This phenomenon is easily noticeable and audible, producing a glowing and continuous current passing through the conductive points. Electric arcs are often seen in various applications, including welding, electrical equipment failures, and in the case of battery packs, as a result of faulty connections between battery cells.
When it comes to EV batteries, the hazards associated with arc flash become even more pronounced; while an electric arc is an underlying phenomenon, an arc flash is a consequential and hazardous discharge accompanying it.
EV batteries can store hundreds of volts of electricity, magnifying the potential risks. A key factor contributing to these heightened risks is the prevalent use of high-voltage lithium-ion batteries in EVs. These batteries are favored due to their exceptional energy density and extended lifespan. However, their high-voltage nature makes them more susceptible to arc flash incidents, underscoring the importance of proper testing and handling of EV batteries.
Siemens’ Simcenter Sound Camera
This distinct noise generated by electric arcs can be used as a diagnostic tool in battery testing. This realization has paved the way for an innovative solution: utilizing advanced technology such as the Simcenter Sound Camera to precisely locate these electric arcs in a battery pack.
According to Siemens, the Simcenter Sound Camera is a tool that can effectively locate these electric arcs, aiding in the repair of battery packs. By analyzing the Overall Sound Pressure Level (OSPL) during testing, peaks can be identified, and the sound camera can precisely pinpoint the location of the defect. This information enables the repair of the battery, resulting in cost savings.

Siemens claims that the localization of the defect cell is exact by using unique techniques of the Simcenter Sound Camera software, such as Bayesian focusing—a microphone array method for sound source localization. The Bayesian Focusing covers the entire frequency range and has broader distance applicability than conventional Nearfield Acoustic Holography techniques. Contrary to other wide frequency band methods, it gives good results for correlated and uncorrelated sources. The sound camera hologram will show the defect location with a red dot. Below are two application examples, where the defect connection of the battery pack has been precisely located.
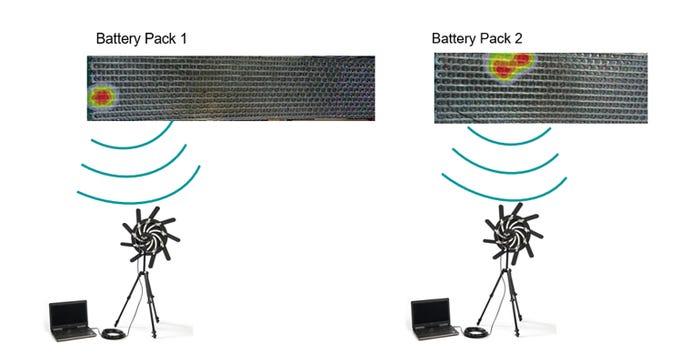
Harnessing the power of electric arcs and their associated sounds could be another way for EV battery manufacturers to enhance the production and maintenance of EV battery packs, contributing to safer and more efficient electric vehicles.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like





